The digital publishing industry has grown in leaps and bounds since the first document was digitized slightly more than half a century ago.
Since Project Gutenberg released a digital version of the US Declaration of Independence in 1971, the digital publishing market’s value grew to $186.8 billion in 2022 and is projected to climb to $367.2 billion by 2030.
The sector has grown rapidly thanks to widespread internet adoption, with nearly two-thirds of the global population actively online. It now encompasses ebooks, music, video, audio, news, video games, mobile apps and more.
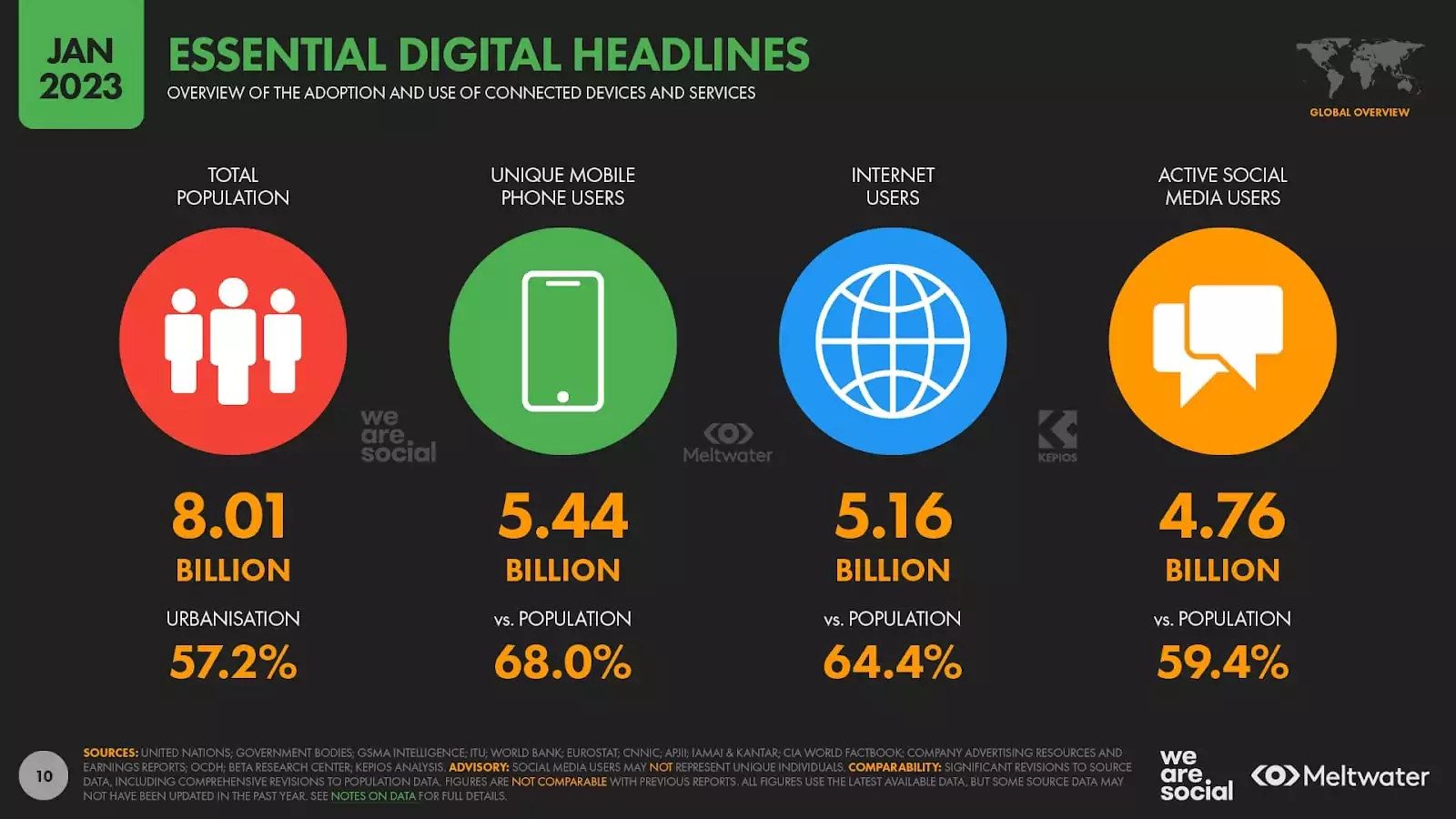
Source: Data Reportal
The digital revolution has made accessing content more effortless and leveled the content creation playing field. There are many tools designed for digital publishers that enable rapid content design, creation and distribution.
With these tools and the proper editorial workflow, individual content creators can just as quickly publish online as a commercial operation, allowing them to build up large followings.
But what is digital publishing? And how does digital publishing work? Let’s dive in.
What Is Digital Publishing?

Digital publishing, sometimes called online or web publishing, involves using online technology to create and share digital content. This content can include websites, ebooks, podcasts, email newsletters and apps.
Publishers can use different digital channels to drive audiences to their content. Social media, content syndication and search engine optimization are all methods of promoting new content.
Digital publishing allows content creators to:
- Reach a wider audience (including mobile users and international audiences)
- Save money relative to the more expensive method of traditional publishing
- Analyze website visitor data and optimize content accordingly
- Collect market research data
Digital Media vs. Print Media
| Digital Media | Print Media | |
| Format | Electronic | Printed on paper |
| Distribution | Websites, email newsletters, social media, app stores | Physical newsstands, bookstores, libraries |
| Production Costs | Content creation carries upfront costs, but distribution costs are much lower. | Same upfront costs for content creation, but physical printing and distribution costs are higher than digital. |
| Accessibility | Instant access is possible via digital devices with an internet connection. | Supply chains determine physical access. |
| Environmental Impact | Digital content’s virtual requirements mean it has a smaller environmental footprint. | Production and distribution of physical media require greater natural resource consumption. |
| Interactivity | Digital content can incorporate interactive features such as video, audio, polls and hyperlinks. | Print materials lack interactive elements. |
| Navigation | Users can leverage search functions and hyperlinks to find desired content quickly. | Physical media requires manual searching with an index or table of contents. |
| Updates | Digital content can quickly and easily be updated and revised. | Updates or revisions require a new print run. |
| Longevity | Publishers can remove access to content unless a third party has backed it up. | Physical books and materials are susceptible to the elements. |
| Cost to Consumers | Depending on publishers’ monetization models, digital content can be more affordable or free. | Physical copies generally cost more. |
While there’s a temptation to declare that print is dead or dying, such statements don’t paint a complete picture. While digital media consumption has proliferated, print books and publications remain central to the media landscape.
Nevertheless, traditional newspapers and print publications can’t offer the same immediacy of access as digital media. Digital news sources provide information more quickly, enabling people to read breaking news as it happens.
For publishers accustomed to print media, the decline of traditional publishing is a big adjustment. As mentioned, however, digital publishing has several advantages.
Digital Publishing Examples
Digital publishing platforms such as WordPress and social media platforms like X (formerly Twitter) and Instagram make online publishing readily accessible for all.
Each time someone posts to Instagram or Snapchat, publishes a tweet or shares their thoughts on Medium, they are part of the digital publishing game. And they’re doing it in large numbers: each day, more than 100 million posts on Instagram and spend 25.7 hours per month on TikTok.
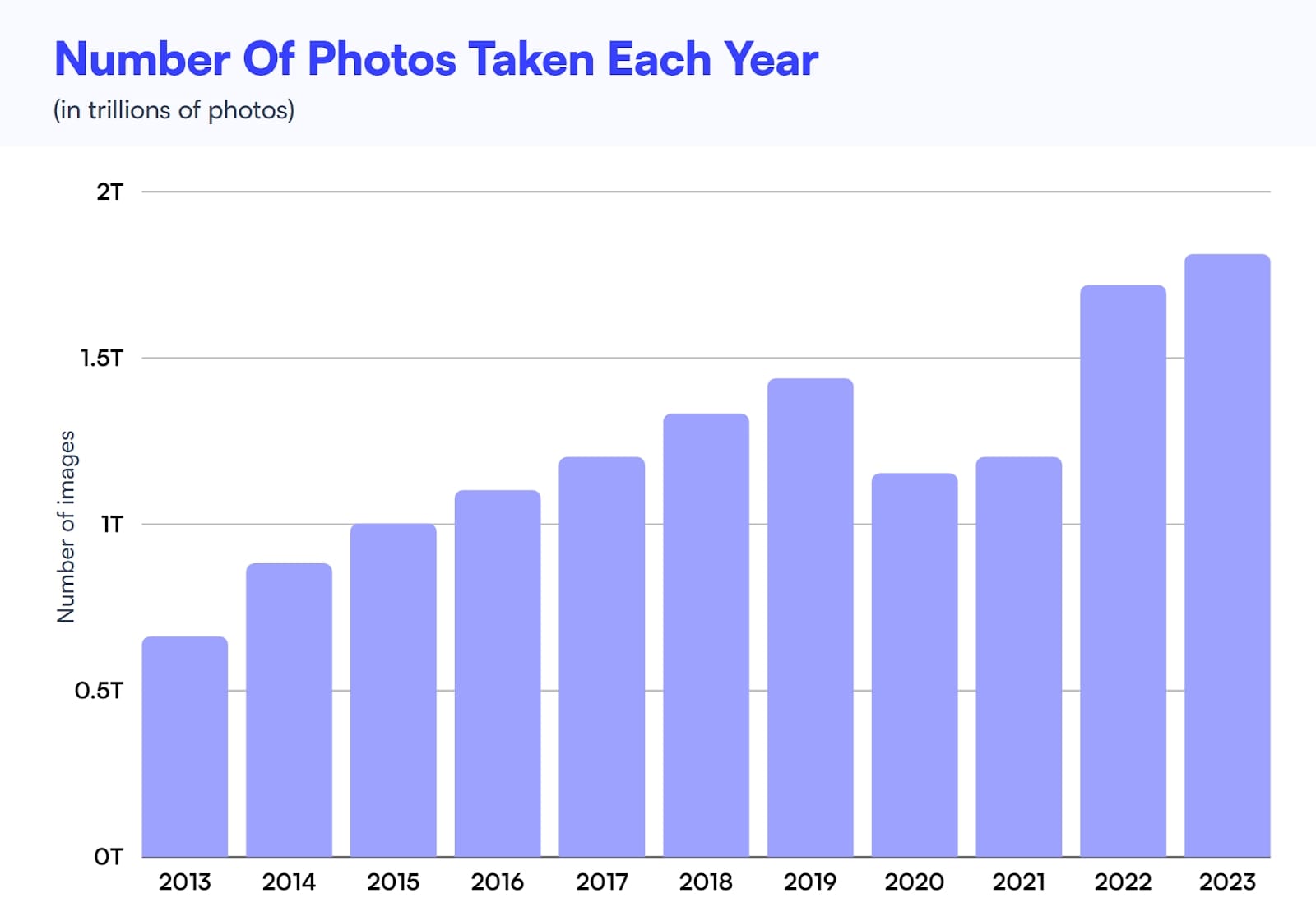
Source: Photutorial
Let’s look at some other common examples of digital publishing.
Online Newspapers

Source: The New York Times
Digital news outlets are, more often than not, one of the first things to spring to mind when thinking about digital publications. These providers
These newspapers provide access to current events, features, sports and more via websites and dedicated news apps. The New York Times is one of the most successful examples, attracting millions of subscribers to its platform.
Digital Magazines

Source: Issuu
Online magazines mimic the look and feel of traditional print publications and are typically accessible via websites, apps and e-readers.
Digital publishing platform Issuu hosts National Geographic’s Expeditions magazine, which captures the feel of leafing through a glossy magazine with double-page spreads. Expeditions avoids cramming interactive elements into its design, limiting most pages to a single hyperlink.
Online Newsletters
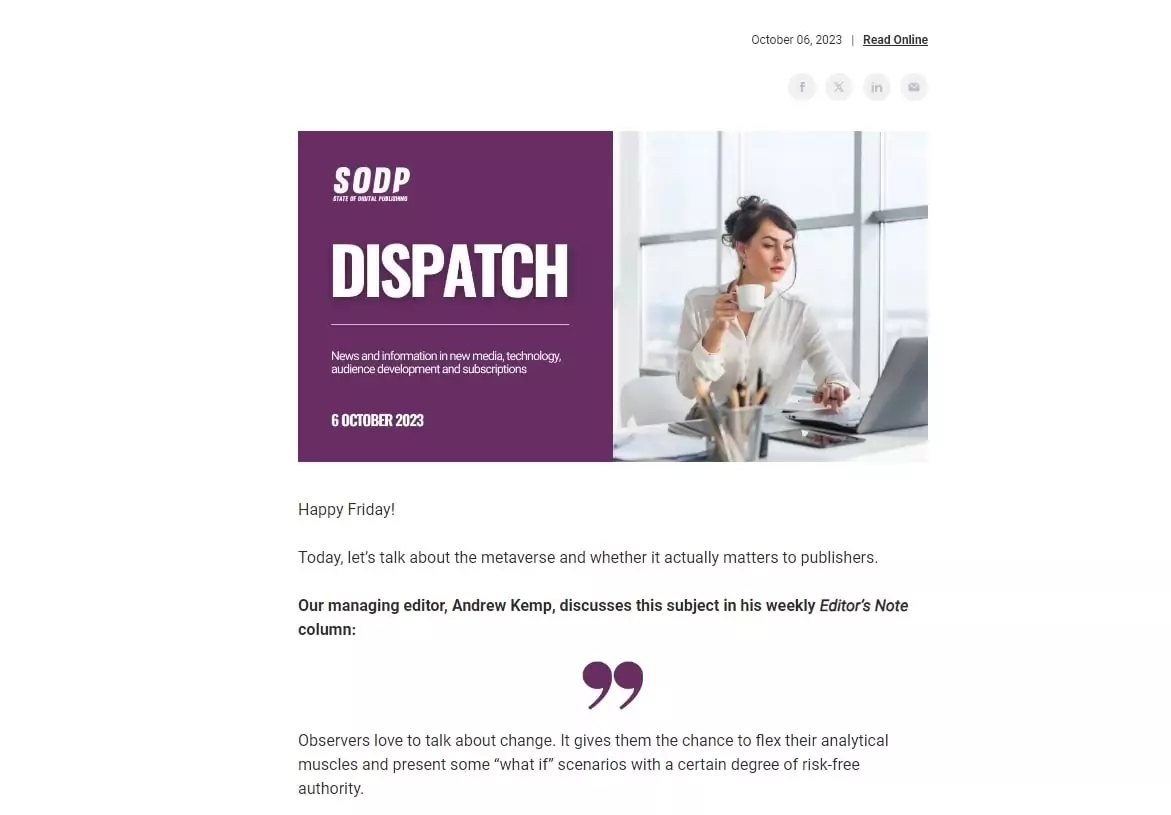
An online newsletter conveys news, updates, or information to subscribers via email or website. An example of this is State of Digital Publishing’s (SODP) weekly Dispatch newsletter, which contains a round-up of our latest stories, some external reading recommendations and industry news bites.
Digital Catalog
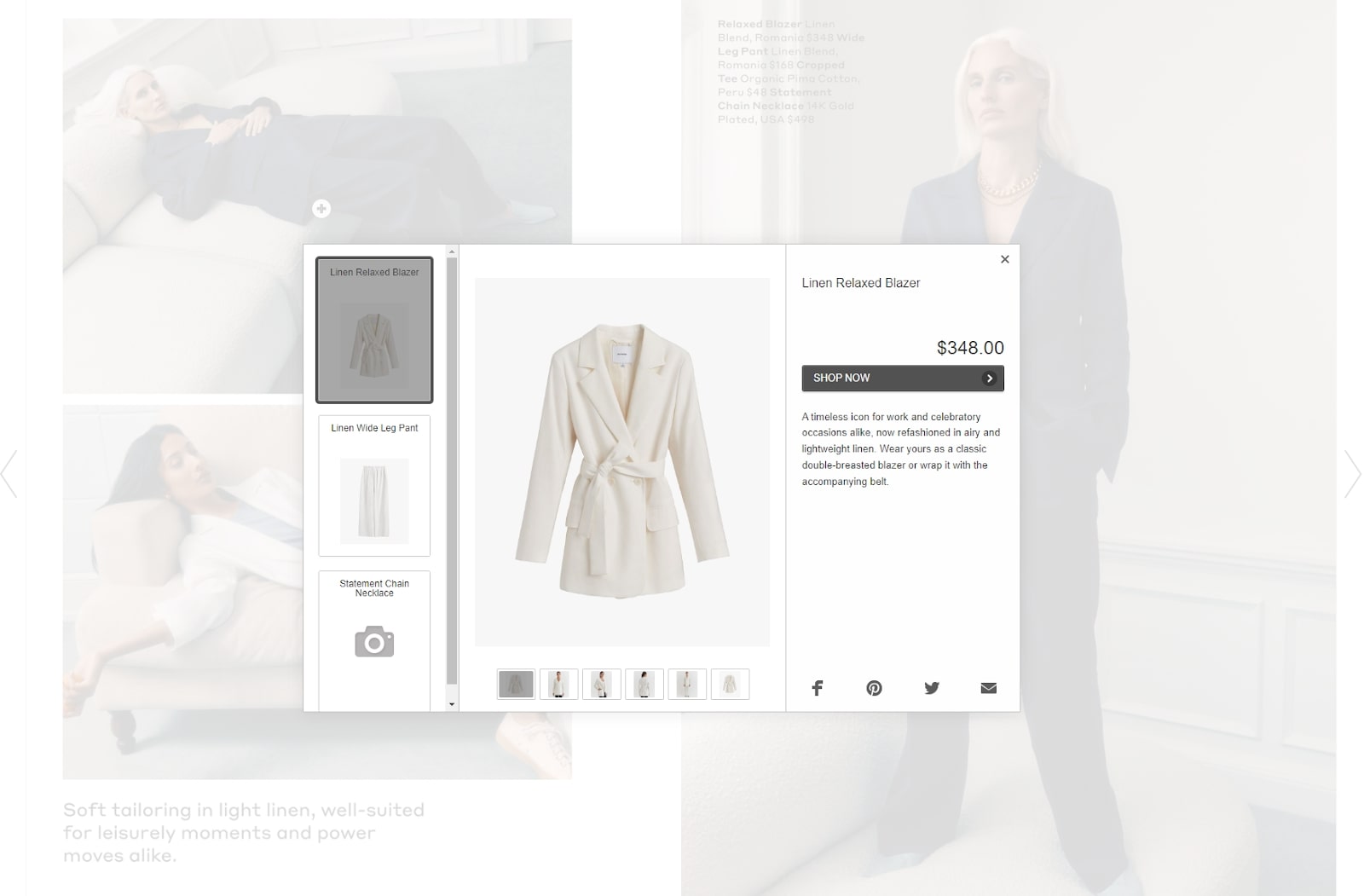
Source: Cuyana
While a digital catalog shows the same product listings and associated images as its physical counterpart, it often contains exclusive interactive features such as “Shop Now” buttons, allowing readers to launch their customer journey.
The above image from Cuyana is an excellent example of this in action, with users able to get more information about the catalog’s showcased looks and even go straight to the online storefront.
eBooks

Source: Amazon
Audiences can read digital books on their computers, laptops, eReaders, tablets and smartphones. Kindle eBooks are the most recognizable example of this format, with readers able to buy and download digital books via Amazon’s digital publishing platform.
Digital Brochures
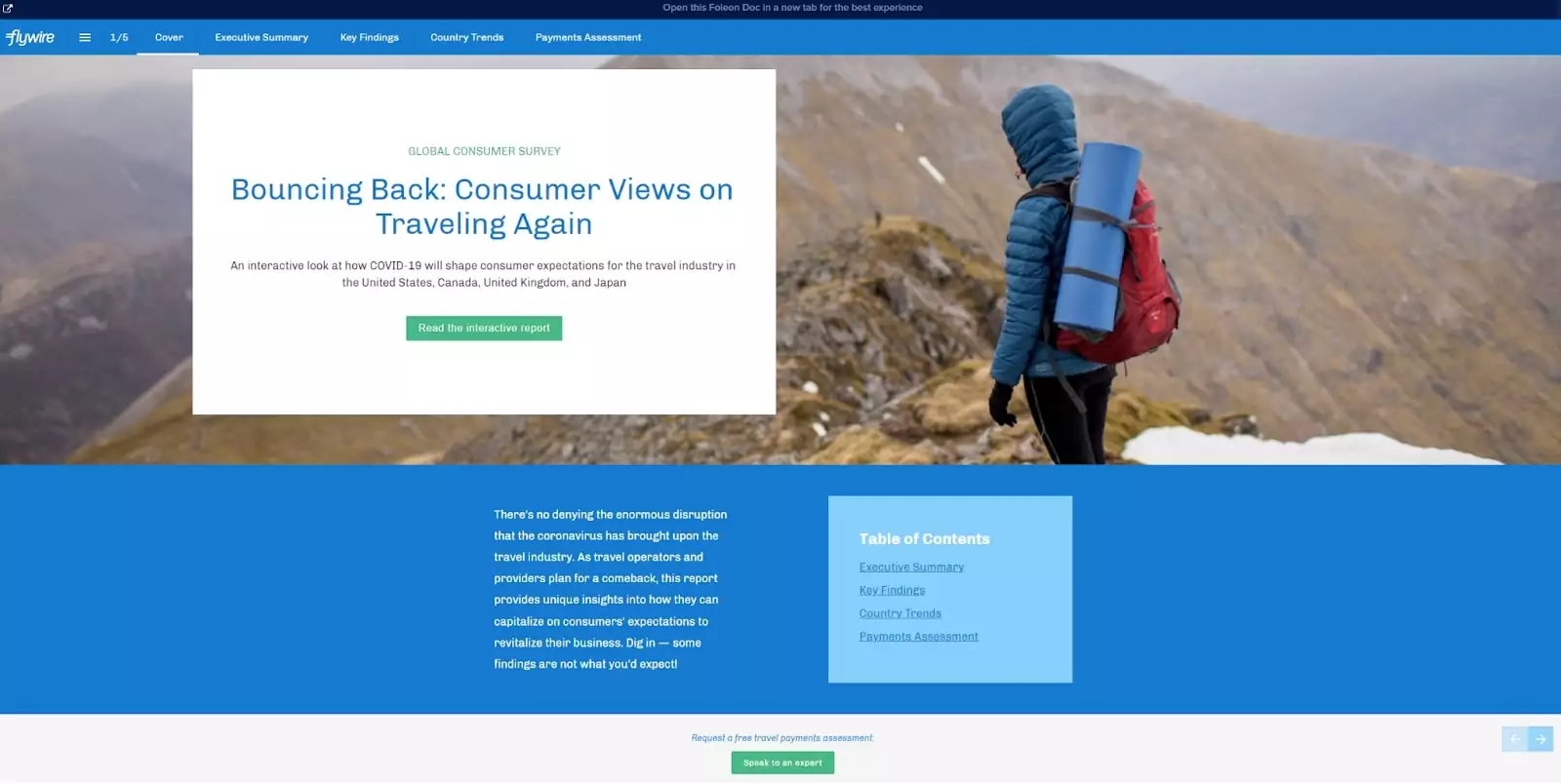
Digital brochures provide information, visuals and details about products, services or organizations.
Flywire’s interactive report from 2020 on COVID-19’s impact on the travel industry is a great example of this in action. Not only did it explore the steps the travel industry needed to take to get back on its feet, but it provided calls to action (CTA) throughout to engage with Flywire for a free travel payments assessment.
Advantages of Digital Publishing
1. Understanding the Audience
Digital media publishers can track a wealth of information about their audience that provides previously unavailable valuable insights.
For example, publishers can track which channels deliver the most visitors, which pages are the least and most popular, and how quickly users exit the site. This data can then inform the content creation process, allowing publishers to address shortcomings in the editorial strategies and double down on areas performing exceptionally well.
There are many site performance metrics publishers should track, including
- Click-through rate (CTR)
- New vs. returning users
- Average time on page
- Scroll depth
- Pages per session
2. Multimedia Integration
Digital publishing can insert more visual and interactive content than traditional methods. Digital natives expect to see videos, infographics, GIFs and links to other media in their content.
The best digital publishing platforms enable publishers to integrate YouTube, Vimeo, SoundCloud and SlideShare into PDFs and whitepapers.
Visual stimulation is rising, with video accounting for almost two-thirds of internet traffic in 2022. At the same time, video content has become a favorite tool among marketers, with 96% considering it an essential part of their marketing strategy.
Visual content encourages readers to spend more time with a website or media channel and is vital to engaging audiences.
3. Cost Savings
By eliminating printing and physical distribution costs, publishers can invest more heavily in content creation and marketing.
They don’t have to worry about paying for paper, ink and distribution or storing unsold inventory that might never sell once subsequent editions come out.
Digital publishing allows media companies to quickly reach new audiences without the associated costs of physically selling copies entering a new city, state or country. At the same time, marketing costs are substantially less.
4. Digital Advertising
Print publishers’ ad layout and format options are relatively limited, while their digital peers have more freedom when experimenting.
Digital advertising supports multimedia elements — such as videos, animations and social media links — encouraging user engagement.
Digital publishers can also A/B test ad formats and layouts to find the best-performing combinations. Successful ad campaigns mean publishers can charge more for future ad placements, maximizing ad revenue.
As noted above, publishers can also build comprehensive and detailed audience profiles, which can then be leveraged to find the best rates for their ad inventory. These profiles contain info browsing habits, location, interests and more, all of which can be used to improve targeted advertising.
Digital publishers can also sell their inventory via programmatic advertising, which automates and streamlines the process.Publishers can offer their available inventory to multiple bidders simultaneously, selling ad slots via automated auctions in the blink of an eye.
5. Social Media Exposure
Digital publishers can increase their visibility by sharing stories via their social media profiles. For example, the last few years have seen a surge in publishers entering TikTok to connect with younger audiences.
Content from our partners
These social media networks allow readers to share content, which can lead to more views, traffic and subscribers.
Digital Publishing Business Models
Digital publishing companies not only have to consider audience building and content creation but also need a clear strategy for monetizing both.
A sustainable business model allows a digital publisher to produce high-quality, relevant online content while increasing its number of advertisers and readers. The following business models are currently the most used by media publishing companies:
1. Advertising
Advertising remains the most popular approach to content monetization because the barriers to entry are relatively low. The publisher has to focus on creating content that drives traffic to their site, which can then be converted into ad impressions and clicks.
As traffic numbers increase, publishers can collaborate with one of the best ad networks to optimize their revenue further.
2. Subscriptions
The subscription or membership model focuses on users who value high-quality, exclusive content and are willing to pay a recurring fee to access it. Paywalls are vital to making this strategy work, limiting non-subscribers’ access.
Publishers value this model because it reduces their reliance on advertising while building audience segments and collecting subscriber data.
3. Affiliate Marketing
Publishers can generate additional revenue using affiliate marketing. Publishers that send traffic to a business via an affiliate link will receive a small percentage of whatever sales the brand gets from those users.
A well-known example of the publisher affiliate model is The New York Times’ Wirecutter, which includes affiliate links along with its product reviews.
4. Sponsored Content
This model involves brands paying publishers to create and promote content that aligns with the brand’s messaging and goals. This approach allows brands to connect with the publisher’s audience more authentically.
5. eCommerce
Retailing and eCommerce models are aimed at consumers interested in purchasing specific products and consuming product-related content.
Final Thoughts
Digital publishing continues to expand and grow. In 2021, 30% of all Americans had read an eBook, up from 17% in 2011. Digital newspapers, meanwhile, continue to see a shift from print to digital editions. For example, of The New York Times’ 9.7 million subscribers, just 710,000 had a print subscription.
We’ve already highlighted the many benefits digital publishing offers, but we can boil the essence of these down to flexibility and opportunity. Digital publishers are more free to experiment with everything from unrestricted word counts to ad layouts and formats.
Digital technology has opened up new ways for publishers to read and engage audiences. This same technology, however, has leveled the playing field, making it easier for new players to enter the space and established players to branch into new segments. With competition rising, publishers must stay abreast of digital publishing trends to develop comprehensive strategies and stand out.













